Introduction to Alfacalcidol and Calcitriol
In recent years, the importance of vitamin D for maintaining optimal health has become more and more apparent. As a result, there has been an increased interest in the various forms of this essential nutrient, particularly the two most commonly prescribed vitamin D analogs - alfacalcidol and calcitriol. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison between these two compounds, shedding light on their similarities, differences, and which one might be more suitable for you. So, let's dive in and explore the world of alfacalcidol and calcitriol.
Understanding the Basics: What are Alfacalcidol and Calcitriol?
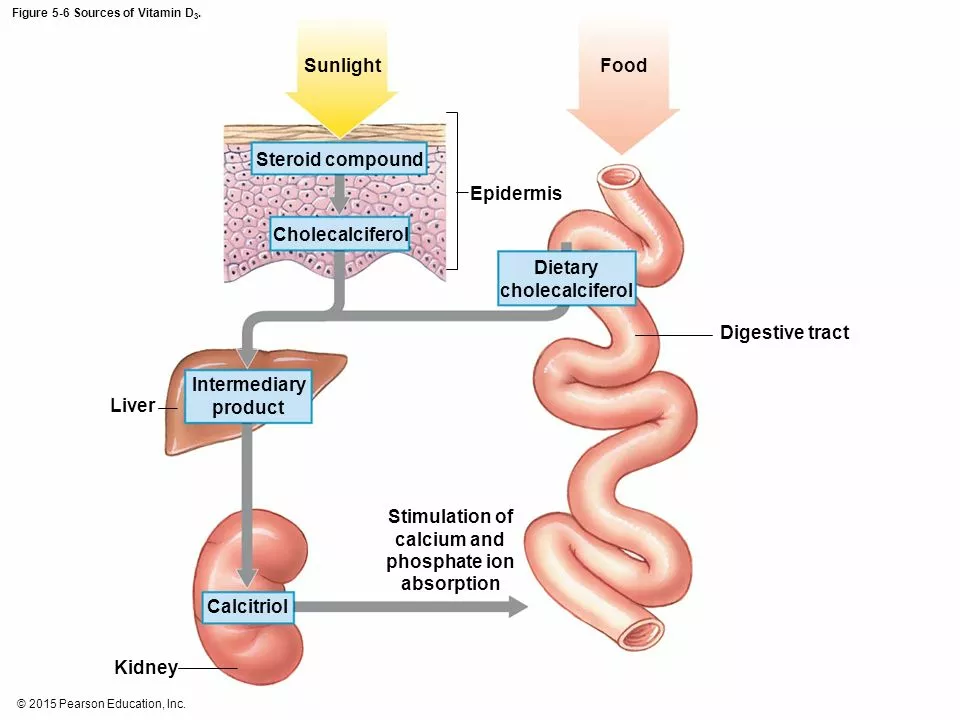
Alfacalcidol and calcitriol are both synthetic forms of vitamin D that are often prescribed to individuals who have a deficiency in this essential nutrient. They are known as vitamin D analogs because they are structurally similar to naturally occurring vitamin D but have some differences in their chemical makeup. This allows them to be more easily absorbed by the body and used more effectively in maintaining healthy levels of calcium and phosphorus in the blood.
Alfacalcidol, also known as 1-alpha hydroxycholecalciferol, is a prohormone that gets converted to calcitriol in the liver. Calcitriol, or 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, is the active form of vitamin D that is responsible for regulating calcium and phosphorus levels in the body. Both of these compounds are used to treat various conditions related to vitamin D deficiency, such as osteoporosis, hypocalcemia, and chronic kidney disease.
Comparing the Mechanism of Action
Although alfacalcidol and calcitriol are both vitamin D analogs, they have slightly different mechanisms of action. Alfacalcidol, being a prohormone, must first be converted into calcitriol in the liver before it can exert its effects on the body. This conversion is regulated by the enzyme 25-hydroxylase, which ensures that the levels of calcitriol remain within a specific range.
Calcitriol, on the other hand, is the active form of vitamin D and can directly interact with the vitamin D receptor (VDR) in target tissues, such as the intestines, kidneys, and bones. This interaction leads to the regulation of calcium and phosphorus absorption, as well as bone mineralization. Therefore, calcitriol is considered to have a more potent and direct effect on the body compared to alfacalcidol.
A Side-by-Side Comparison: Efficacy and Safety
When it comes to the efficacy and safety of alfacalcidol and calcitriol, several studies have been conducted to compare their performance in treating various conditions related to vitamin D deficiency. Overall, both compounds have been shown to be effective in increasing calcium and phosphorus levels in the body, as well as improving bone mineral density.
However, some studies have suggested that calcitriol may have a slightly higher efficacy in treating certain conditions, such as secondary hyperparathyroidism, compared to alfacalcidol. This is likely due to calcitriol's more direct mechanism of action, as it does not require conversion in the liver before it can exert its effects.
In terms of safety, both alfacalcidol and calcitriol have been well-tolerated in most individuals, with few reported side effects. However, calcitriol may have a higher risk of causing hypercalcemia (high calcium levels in the blood) compared to alfacalcidol, particularly when used in high doses. This is because calcitriol has a more potent effect on calcium and phosphorus regulation, which can sometimes lead to an imbalance in blood levels.
Choosing the Best Vitamin D Analog for You
The choice between alfacalcidol and calcitriol ultimately depends on the specific needs of the individual and their medical history. In some cases, alfacalcidol may be preferred due to its lower risk of causing hypercalcemia, particularly in individuals with a history of high calcium levels or those who require long-term supplementation. Additionally, alfacalcidol may be more suitable for individuals with liver impairment, as it does not require conversion in the liver to become active.
Conversely, calcitriol may be more appropriate for individuals who require a more potent and direct effect on calcium and phosphorus regulation, such as those with secondary hyperparathyroidism. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate vitamin D analog for your specific needs and to ensure proper dosing and monitoring throughout the course of treatment.
Conclusion: Alfacalcidol and Calcitriol - Two Effective Vitamin D Analogs
In conclusion, both alfacalcidol and calcitriol are effective vitamin D analogs that can be used to treat various conditions related to vitamin D deficiency. While they have some differences in their mechanisms of action, efficacy, and safety profiles, both compounds have been shown to be well-tolerated and effective in improving calcium and phosphorus levels in the body, as well as bone mineral density.
The choice between alfacalcidol and calcitriol ultimately depends on the specific needs of the individual and their medical history. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate vitamin D analog and to ensure proper dosing and monitoring throughout the course of treatment. By doing so, you can effectively address any vitamin D deficiencies and work towards maintaining optimal health.






Comments(7)